Computer architecture refers to the end-to-end structure of a computer system that determines how its components interact with each other in helping to execute the machine’s purpose (i.e., processing data).
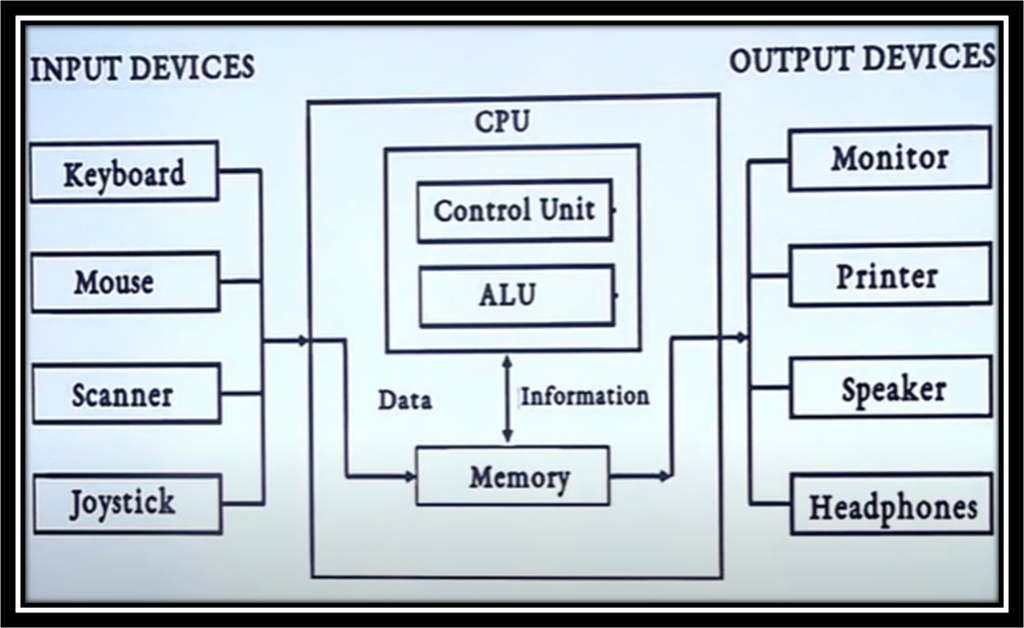
Components of computer
- Input Unit
- Output Unit
- Central Processing Unit
- Memory Unit
Input Unit
The computer accepts coded information through input unit by the user. It is a device that is used to give required information to the computer.
Example : Keyboard, mouse, etc.
An input unit performs the following functions :
- It accepts the instructions and data from the user.
- It converts these instructions and data in computer in acceptable format.
- It supplies the converted instructions and data to the computer system for further processing.
Output Unit
This unit sends the processed results to the user. It is mainly used to display the desired result to the user as per input instruction.
Example : Monitor, printer, plotter, etc.
The following functions are performed by an output unit :
- It accepts the results produced by the computer which are in coded form and hence cannot be easily understood by user.
- It converts these coded results to human acceptable form.
- It supplies the converted results to the user
Central Processing Unit(CPU)
It consists a set of registers, arithmetic logic unit and control unit, which together interpret and execute instructions in assembly language.
The primary functions of the CPU are as follows :
- The CPU transfers instructions and input data from main memory to registers, i.e. internal memory.
- The CPU executes the instructions in the stored sequence.
- When necessary, CPU transfers output data from registers to main memory.
Central Processing Unit is often called the brain of computer. The CPU is fabricated as a single Integrated Circuit (IC) and is also known as microprocessor.
A CPU controls all the internal and external devices and performs arithmetic and logic operations.
The CPU consists of following main sub-systems :
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
- Control Unit (CU)
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
ALU contains the electronic circuitry that executes all arithmetic and logical operations on the available data. ALU uses registers to hold the data that is being processed.
Most ALUs can perform the following operations :
(i)Logical operations (AND, NOT, OR, XOR).
(ii)Arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division).
(iii)Bit-shifting operations (shifting or rotating a word by a specified number of bit to the left or right with or without sign extension).
(iv)Comparison operations (=, <, <=, >, > =)
Control Unit (CU)
CU coordinates with the input and output devices of a computer. It directs the computer to carry out stored program instructions by communicating with the ALU and the registers.
It organises the processing of data and instructions.
The basic function of control unit is to fetch the instruction stored in the main memory, identify the operations and the devices involved in it and accordingly generate control signals.
Memory Unit
This unit is responsible to store programs or data on a temporary or permanent basis. It has primary memory (main memory) and secondary memory (auxiliary memory).
The input data which is to be processed is brought into main memory before processing
Another kind of memory is referred to as secondary memory of a computer system. This unit is used to permanently store data, programs and output. This unit does not deal directly with CPU.
Motherboard
The main circuit board contained in any computer is called a motherboard.
It is also known as the main board or logic board or system board or planar board.
All the other electronic devices and circuits of computer system are attached to this board like, CPU, ROM, RAM, expansion slots, PCI slots and USB ports. It also includes controllers for devices like the hard drive, DVD drive, keyboard and mouse. In other words, motherboard makes everything in a computer work together.
Components on Motherboard
Various components on motherboard are as follows
(i)CMOS Battery
(ii) BIOS Chip
(iii) Fan
(iv)Expansion Slot
(v)SMPS
(vi)PCI Slot
(vii) Processor Chip
(viii) Buses
Interconnection of Units
CPU sends data, instructions and information to the components inside the computer as well as to the peripheral devices attached to it.
A bus is a set of wires used for interconnection, where each wire can carry one bit of data.
In other words, bus is a set of electronic signal pathways that allows information and signals to travel between components inside or outside of a computer.
A computer bus can be divided into two types :
1.Internal bus
2.External Bus
1.Internal Bus
The internal bus connects components inside the motherboard like CPU and system memory. It is also called the system bus.
Internal bus includes following buses :
•The command to access the memory or the I/O devices is carried by the control bus.
•The address of I/O devices or memory is carried by the address bus. The data to be transferred is carried by the data bus.
2. External Bus :
It connects the different external devices, peripherals, expansion slots, I/O ports and drive connections to the rest of computer. It is also referred to as the expansion bus.
Instruction Cycle
A simple instruction cycle consists of the following Steps :
1.Fetching the instruction from the memory.
2.Decoding the instruction for operation.
3.Executing the instruction.
4.Storing in memory.
In above steps,
step 1 and 2 instructions are same and known as fetch cycle and
step 3 and 4 instructions are different and known as execute cycle
Instructions Format
Computer understands instructions only in terms of 0’s and 1’s, which is called the machine language.
A computer program is a set of instructions that describes the steps to be performed for carrying out a computational task.
The processor must have two inputs; instructions and data.
The instructions tell the processor what actions are needed to be performed on the data.
An instruction is further divided into two parts:
operation (op-code) and operand.
The op-code represents action that the processor must execute and operand defines the parameters of the action and depends on the operation
| Download Notes | Click here |
| Download Worksheet | Click here |





thank you so much sir